coal hardness
-
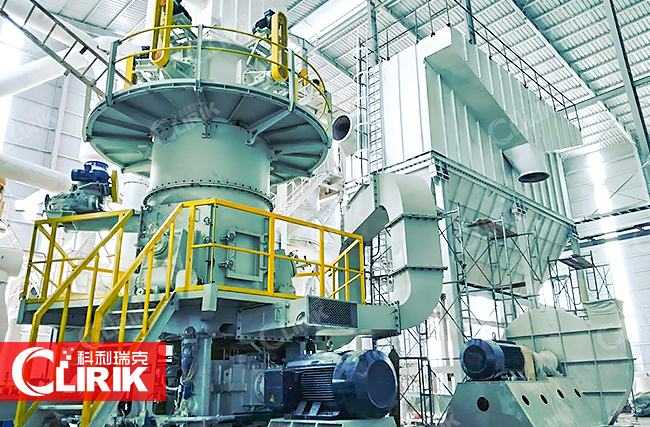

Ultra Fine Pulverizer
Ultra fine pulveriser which we also called super fine pulverizer, micro powder pulverizer, because they can produce 2500 mesh powder.
-
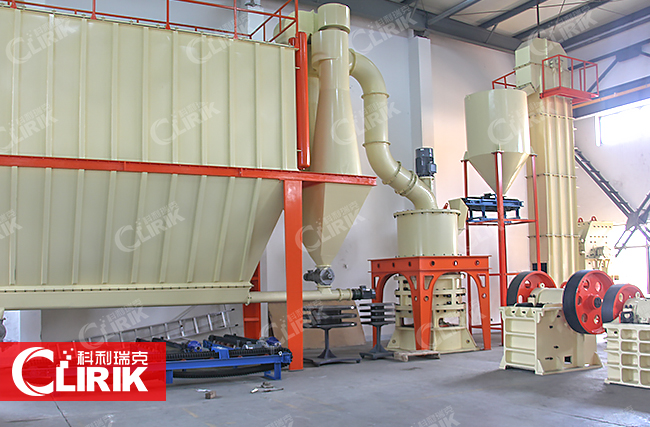

Micro pulverizer
CLIRIK micro pulverizer, which is designed by our engineers and technicians on the basis of multiple innovation, test and experience over two decades, has absorbed many advantages of home and abroad mill manufacturing technique.
-
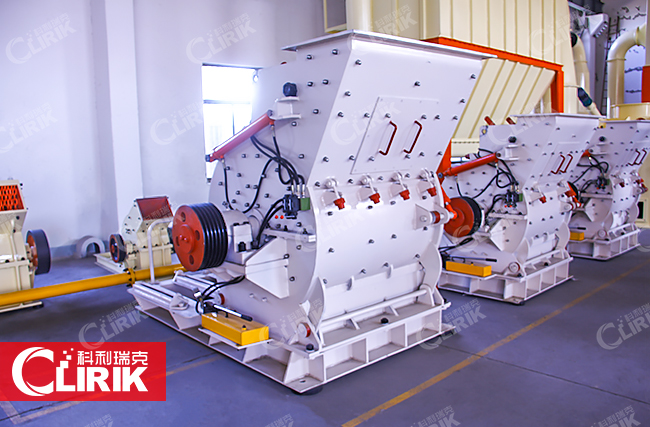

PC series hammer crusher
Hammer crusher is equipment using high-speed rotary hammers to crush materials, mainly applied to the industries of metallurgy, mining, chemistry, cement, construction, refractory materials and ceramics.
-
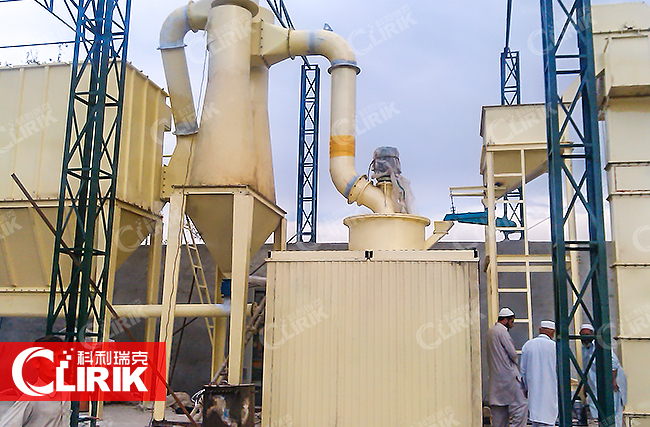

HGM series pulverizer
HGM series pulverizer is for super-fine grinding materials with hardness less than 6 in Moh' s scale and humidity less than 6 percent such as kaolin, limestone, calcite, marble,talcum, barite, gypsum,
-
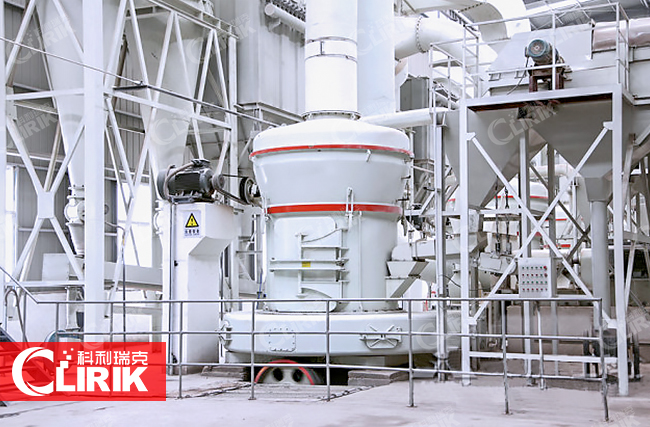

Raymond Pulverizer
YGM series Raymond Pulverizer has the similar working principle as Raymond mill, but its grinding device is fixed with 1000-1500kg pressure springs.
-
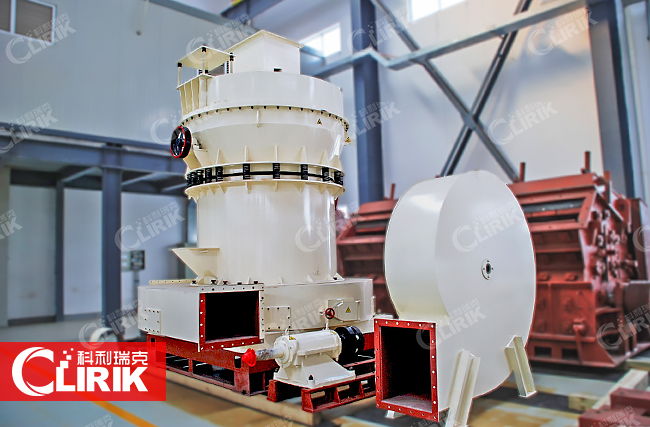

HGM 80 stone pulverizer
The whole set HGM80 stone pulverizer consists of hammer crusher, bucket elevator, storage hopper, vibrating feeder, main unit, inverter classifier, cyclone collector, pulse deduster system, high pressure positive blower,
-
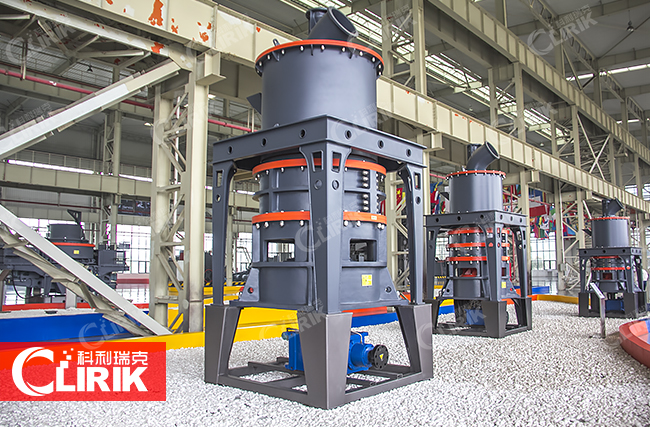

HGM 90 rock pulverizer
HGM 90 rock pulverizer is for super-fine grinding materials with hardness less than 6 in Moh‘s scale and humidity less than 6 percent such as kaolin, limestone, basalt, calcite, marble, talcum, barite, gypsum, dolomite,
-
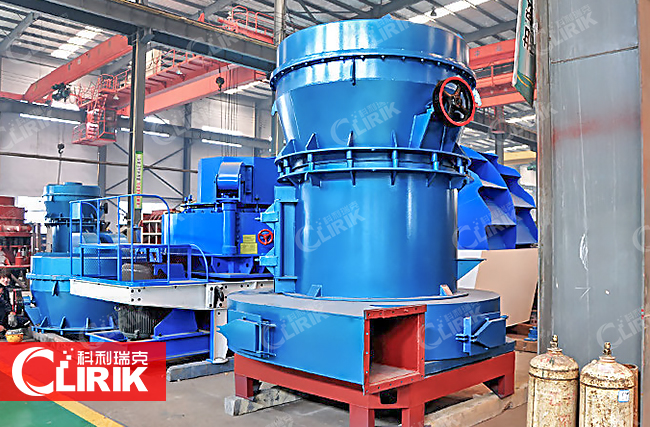

Gypsum Pulverizer
Gypsum is a very soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It can be used as a fertilizer, is the main constituent in many forms of plaster and is widely mined.